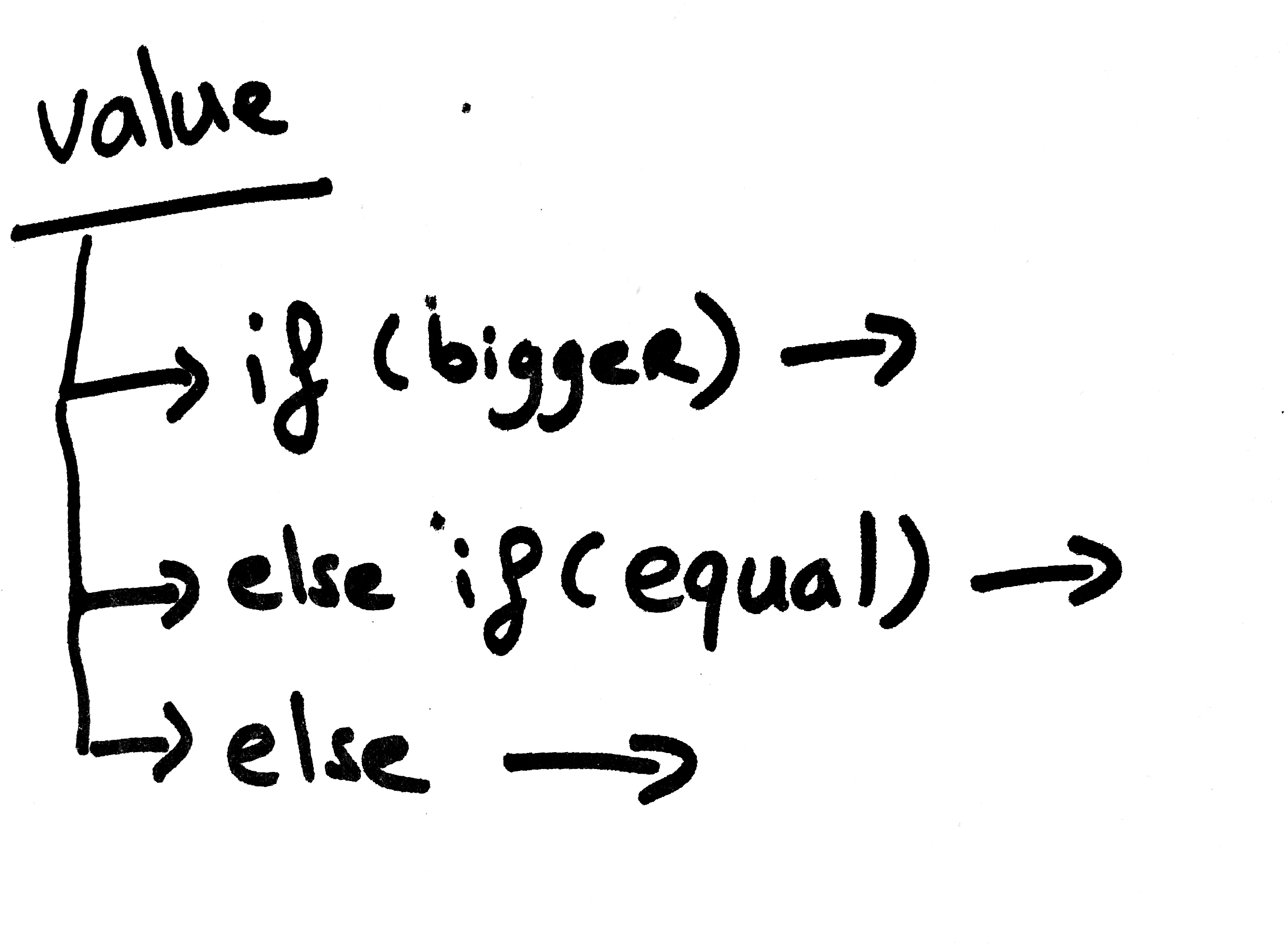In Java you can make choices with an if-statement. Actually, you ask the computer something.
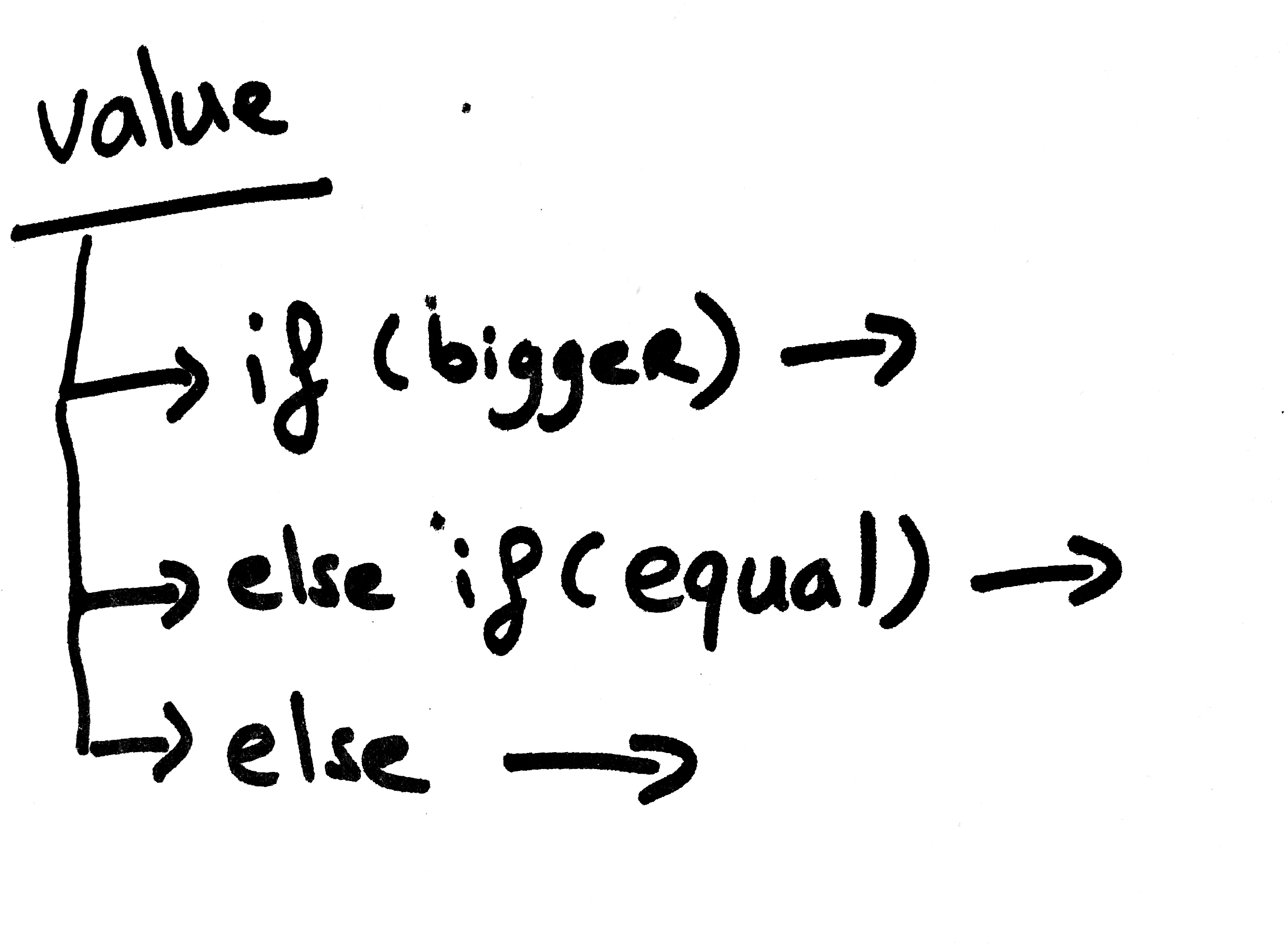
THEORY
- For the first question use: if + ( + condition + ) + { + }
if ( is value bigger than 10 )
{
//you end up in this block of code
}
- For all questions in between use: else if + ( + condition + ) + { + }
else if ( is value smaller than 10 )
{
//you end up in this block of code
}
- For the last question use: else + { + }
else
{
//you end up in this block of code
}
example 1
We want that the program calculates if the value of “number” is bigger, smaller or equal than 10.
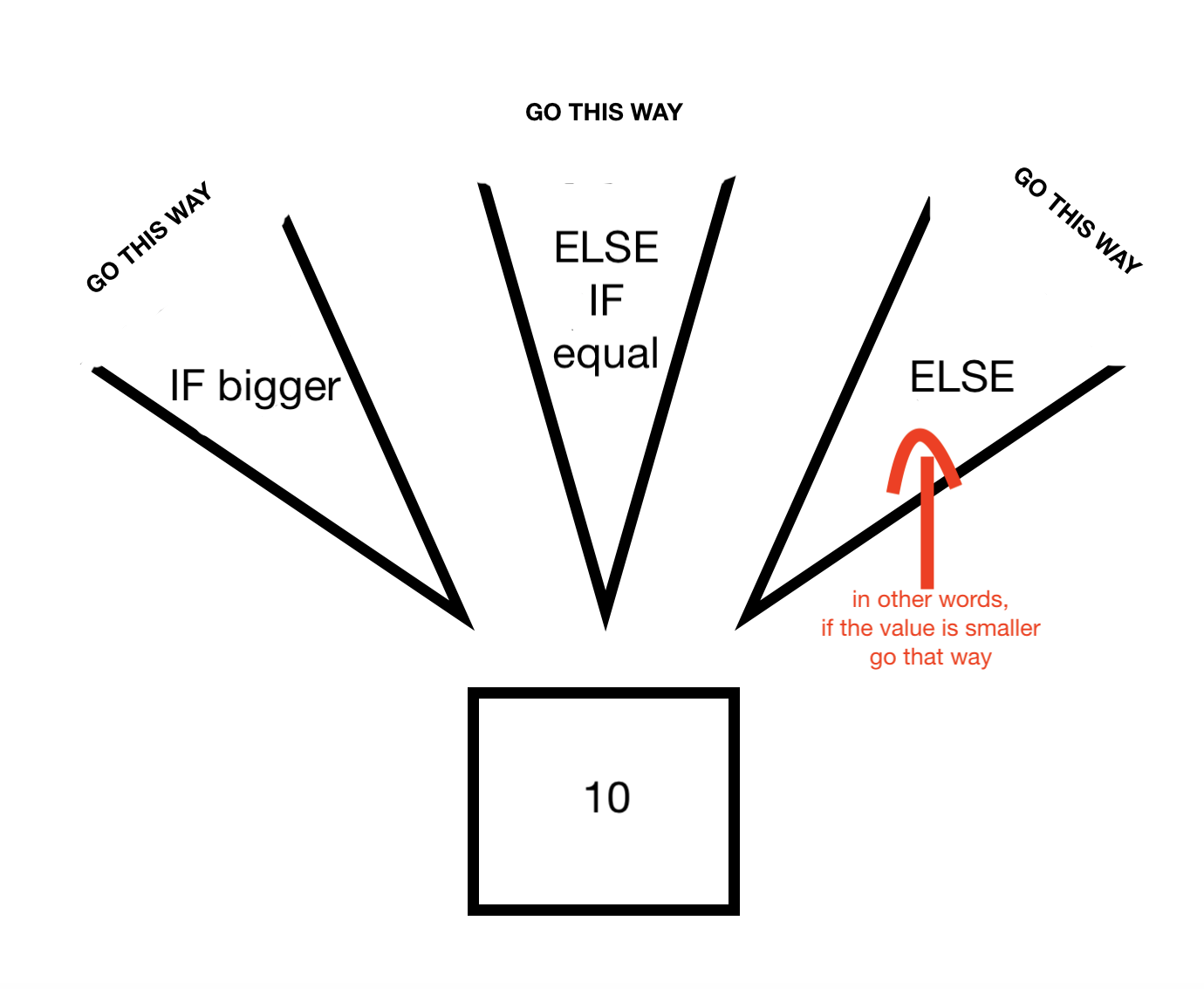
if (number > 10)
{
//number is bigger than 10
}
else if (number == 10)
{
//number is equal to 10
}
else
{
//number is smaller than 10
}
Normally programmers write it like this:
if (number > 10) {
//number is bigger than 10
} else if (number == 10) {
//number is equal to 10
} else {
//number is smaller than 10
}
EXAMPLE 2
REMARK: working with objects or String; then you should you use the method equals() instead of ==:
if (word.equals("what sup") {
//word is "what sup"
} else {
//word is not "what sup"
}
More Conditions:
You can also do an if-statement with two conditions, using logical operators.
example
void start() {
int number = 30, number2 = 20, number3 = 30;
if (number > number2 && number < number3) {
System.out.printf("%d is between %d and %d ", number, number2, number3);
} else if (number > number2 && number > number3) {
System.out.printf("%d is bigger than %d and %d", number, number2, number3);
} else {
System.out.printf("%d is not in between %d and %d or bigger than %d and %d", number, number2, number3, number2, number3);
}
}
30 is smaller than 20 and equal to 30, therefore the output should be, the last else:
output: 30 is not in between 20 and 30 or bigger than 20 and 30